As How Climate Change Is Affecting Insurance Rates takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with engaging insights into the intricate relationship between climate change and insurance rates. By delving into the nuances of this pressing issue, readers are poised to unravel a narrative that sheds light on the impact of climate change on insurance premiums.
The subsequent paragraph will delve deeper into the specifics of how climate change is intricately linked to the fluctuations in insurance rates across various sectors.
Overview of Climate Change and Insurance Rates
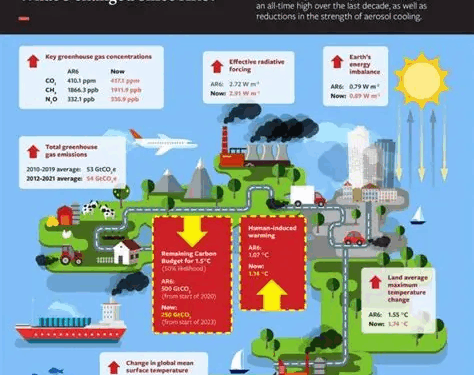
Climate change refers to the long-term alteration of temperature and typical weather patterns in a specific region or globally. This phenomenon is primarily driven by human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, leading to an increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.The impact of climate change on insurance rates is significant and undeniable.
As extreme weather events become more frequent and severe due to climate change, insurance companies are facing higher costs associated with property damage, crop loss, and other claims. This, in turn, leads to an increase in insurance premiums for policyholders.
Specific Insurance Types Affected by Climate Change
- Property Insurance: Increased frequency of hurricanes, wildfires, and floods due to climate change has led to higher payouts for property insurance companies, resulting in higher premiums for homeowners.
- Crop Insurance: Changing weather patterns and prolonged droughts are impacting crop yields, leading to increased claims for crop insurance providers and subsequently higher premiums for farmers.
- Flood Insurance: Rising sea levels and increased precipitation are contributing to more frequent and severe flooding events, affecting flood insurance rates for homeowners and businesses located in high-risk areas.
Factors Contributing to Increased Insurance Rates
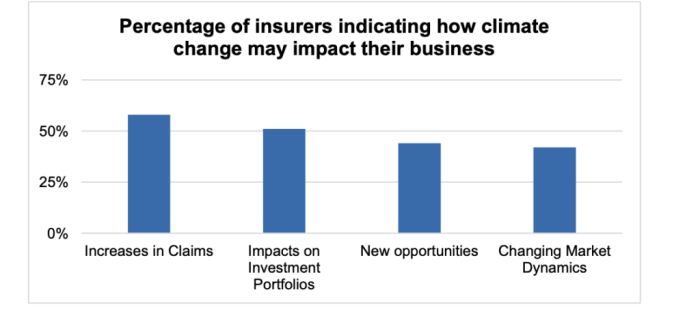
Extreme weather events play a significant role in the rising costs of insurance. As climate change leads to more frequent and severe hurricanes, floods, wildfires, and other natural disasters, insurance companies face higher payouts, resulting in increased premiums for policyholders.
Impact of Changing Climate Patterns
- Changing climate patterns are directly influencing insurance premiums by causing shifts in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events.
- Insurers must adjust their risk models and pricing strategies to account for the evolving climate conditions, leading to higher costs for consumers.
- Regions that were once considered low-risk may now face heightened exposure to climate-related hazards, driving up insurance rates in those areas.
Other Factors Affecting Insurance Rates
- Urbanization and infrastructure development in vulnerable areas can increase the likelihood of property damage from natural disasters, impacting insurance costs.
- Technological advancements have allowed for more accurate assessment of risk, but they have also revealed previously underestimated exposures, contributing to higher premiums.
- Legal and regulatory changes, such as new building codes or environmental protection laws, can influence insurance rates by affecting the cost of claims and coverage requirements.
Insurance Industry Response to Climate Change

Insurance companies are actively adapting to the challenges posed by climate change by implementing various strategies to mitigate risks associated with the changing climate. These companies have recognized the need to innovate and develop new insurance products to address the evolving landscape of climate-related risks.
Strategies to Mitigate Risks
- Implementing advanced risk modeling techniques to better assess and price climate-related risks.
- Encouraging policyholders to adopt sustainable practices through discounts or incentives.
- Collaborating with climate scientists and researchers to better understand and anticipate future climate impacts.
Innovative Insurance Products
- Parametric insurance policies that pay out based on predetermined triggers like extreme weather events.
- Microinsurance products tailored for low-income communities vulnerable to climate-related disasters.
- Green insurance options that provide coverage for renewable energy installations or sustainable building practices.
Impact on Policyholders
As insurance rates continue to rise due to the impact of climate change, policyholders are facing significant financial challenges. The increased frequency and severity of natural disasters are leading to higher premiums and deductibles, making it harder for individuals to afford adequate coverage.
Financial Strain on Policyholders
The rising insurance rates are putting a financial strain on policyholders, especially those living in high-risk areas prone to extreme weather events. Many policyholders are finding it difficult to keep up with the increasing costs of insurance, leading to potential gaps in coverage or even cancellation of policies.
- Policyholders may have to allocate more of their budget towards insurance premiums, leaving less money for other essential expenses.
- Some policyholders may be forced to choose between paying for insurance or investing in mitigation measures to protect their properties.
- Policyholders who are unable to afford insurance may face significant financial losses in the event of a disaster, putting their financial stability at risk.
Potential Changes in Coverage or Policy Terms
As climate change continues to impact the frequency and severity of natural disasters, insurance companies may start implementing changes in coverage or policy terms to mitigate their risks. Policyholders should be aware of these potential changes and how they may affect their coverage.
- Insurance companies may introduce higher deductibles or lower coverage limits to manage their exposure to climate-related risks.
- Some insurance policies may exclude certain types of natural disasters or events caused by climate change, requiring policyholders to purchase additional coverage.
- Premiums for properties in high-risk areas may increase significantly, making it challenging for policyholders to maintain adequate coverage.
Tips for Policyholders
Policyholders can take proactive steps to navigate increasing insurance costs and ensure they have adequate coverage in the face of climate change-related risks. Here are some tips to help policyholders manage their insurance needs:
- Regularly review and update your insurance coverage to account for changes in climate-related risks and property values.
- Invest in mitigation measures to reduce the risk of damage to your property and potentially lower your insurance premiums.
- Shop around and compare insurance quotes from different providers to find the best coverage options at competitive rates.
Last Recap
In conclusion, the discourse on How Climate Change Is Affecting Insurance Rates encapsulates a myriad of challenges and opportunities for both insurers and policyholders alike. By navigating the evolving landscape of insurance in the face of climate change, stakeholders can adapt and thrive in a rapidly changing environment.
FAQ Resource
How does climate change impact insurance rates?
Climate change leads to more frequent and severe weather events, resulting in higher insurance claims and subsequently increased rates.
Are there any other factors besides weather that affect insurance rates due to climate change?
Yes, factors like rising sea levels, wildfires, and changing ecological patterns also contribute to the impact on insurance rates.
How are insurance companies adapting to climate change challenges?
Insurance companies are implementing risk mitigation strategies, developing innovative products, and reassessing coverage terms to address climate change risks.
What tips can policyholders follow to navigate increasing insurance costs?
Policyholders can explore bundling policies, increasing deductibles, and investing in home improvements to mitigate insurance cost increases.